By this time, news stories have made words like bugs, viruses and malware familiar and by all means frequent, as computer users scramble to self-educate on how to avoid falling victim to a range of security invasions.
Now "Malvertisers" can be added to the list of mischief-makers who keep security watchers on their toes. Ars Technica's headline was a case in point. "Malvertisers target Mac users with steganographic code stashed in image." HTML5 coding helped malicious ads avoid scanners. Eliya Stein of Confiant explained what we are now facing. According to the Confiant blog, it was Confiant and Malwarebytes which spotted this steganography-based ad payload.
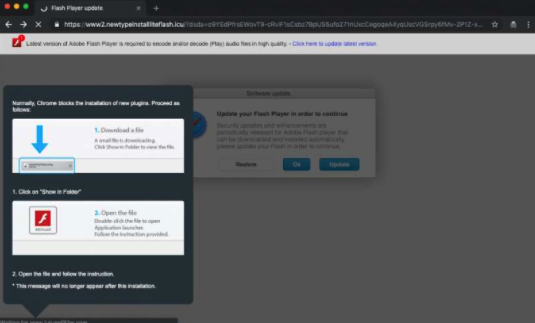
Confiant named the payload as VeryMal. Confiant reported brazenly run display ads under the guise of Flash updates and PC repair software.
Shaun Nichols in The Register presented the problem as "a malvertising operation that spreads through poisoned ad images."
Dan Goodin in Ars Technica reported that "a two-day blitz triggered as many as 5 million times per day. At the core of the storm was "highly camouflaged JavaScript stashed in images to install a trojan on visitors' Macs."
Ionut Ilascu in BleepingComputer similarly reported Confiant said that this recent VeryMal campaign "lasted for two days between January 11-13, and targeted only US visitors."
The sneaky feats were taking advantage of a JavaScript vulnerability on Macs to redirect browsers to a site "where you get the opportunity to install a Flash 'update'. It looks to have been most active between January 11th and 13th, but evidence suggests it was active since December," said PC Perspective.
BleepingComputer reported: "An analysis from Adam Thomas of Malwarebytes shows that the phony update is a macOS adware installer known as Shlayer."
Reports said this was a steganography-based ad payload dropping a Shlayer Trojan on people using Macs.
Read Complete Article: https://techxplore.com/news/2019-01-verymal-campaign-image-based-malware.html